LinkedIn needs no introduction. Simply put, it is a powerful social networking platform used by professionals across the globe to connect, engage, and grow their careers. With more than 900 million users, LinkedIn is a goldmine of information, job opportunities, and professional connections. However, finding the right people, jobs, and information on LinkedIn can be daunting, especially if you’re unfamiliar with the platform’s search capabilities. That’s where Boolean search comes in: it’s a powerful search technique that lets you find what you’re looking for on LinkedIn by combining keywords and search operators.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the basics of Boolean search on LinkedIn and provide tips, tricks, and examples to help you get the most out of this powerful tool.
What is Boolean Search?
As the name indicates, LinkedIn Boolean Search is a search technique that enables you to refine your search results by using a string of modifiers or logical operators to combine, group, or exclude keywords and phrases. It allows you to enter multiple keywords into one search query and narrow the results based on those keywords. Now you can easily find the right people matching certain industries, companies, locations, expertise, or job title. The Boolean search can be used on all LinkedIn search engines, including Basic, Sales Navigator, and Recruiter. All you need to do is enter your keywords and the search operators in all search fields, including titles, company names, profiles, and groups. To further narrow down your results, leverage advanced search filters.
The following are the five LinkedIn Boolean search operators that you can leverage to refine your search results:
- AND
- OR
- NOT
- Quotes – “”
- Parenthesis – ()
How to Use the 5 LinkedIn Boolean Search Operators
Boolean search operators create more specific and targeted search queries on LinkedIn. These operators allow you to combine search terms and modify your search to produce more accurate results. Here are some of the ways to use Boolean search operators and construct your searches:
1. Quotation Marks – “”
Quotation marks are used when searching for an exact phrase rather than individual words. For example, if you are searching for candidate profiles related to “software developer” (with the words in that exact order), you would use quotation marks to specify the phrase.
The search query will be: “Software Developer”.
This will provide only the candidate profiles that contain the exact phrase “software developer”.
Some other examples include:
- “Marketing Manager”
- “Sales Manager”
- “Senior Marketing Manager”

2. AND
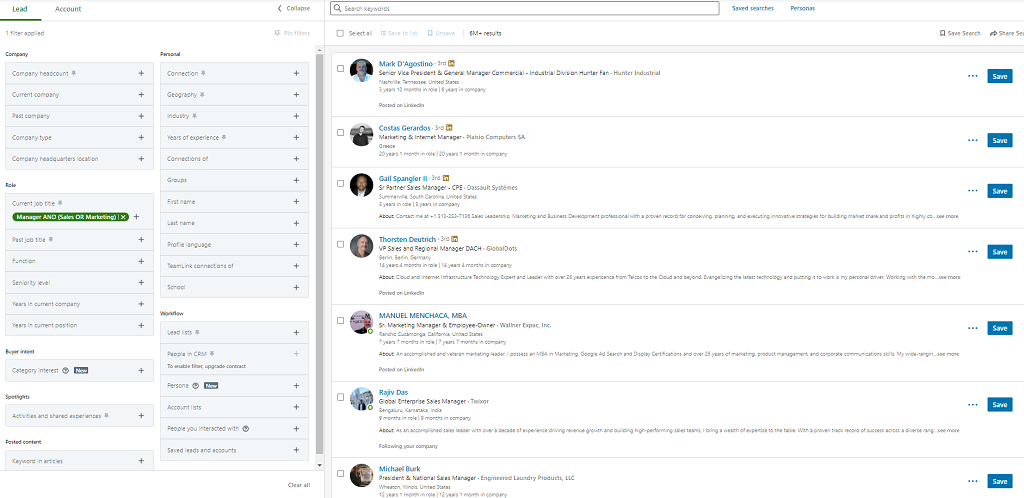
The AND operator is used to get results that include both the search keywords. For example, if you are searching for prospective candidates working as Software Developers and want to find only those working in the Financial Services sector. This is where the AND operator proves promising. You can leverage the AND operator to include both search terms.
The search query would look like “Software Developer” AND “Financial Services”.
This will only give the results of people in this specific job role (Software Developer) and those in this specific industry (Financial Services). The more AND operators you include in your search query, the more targeted and relevant the search results will be. However, you must be mindful that a super-targeted search query may lead to no results.
Some other examples include:
- Sales AND Marketing
- “Marketing Manager” AND B2B

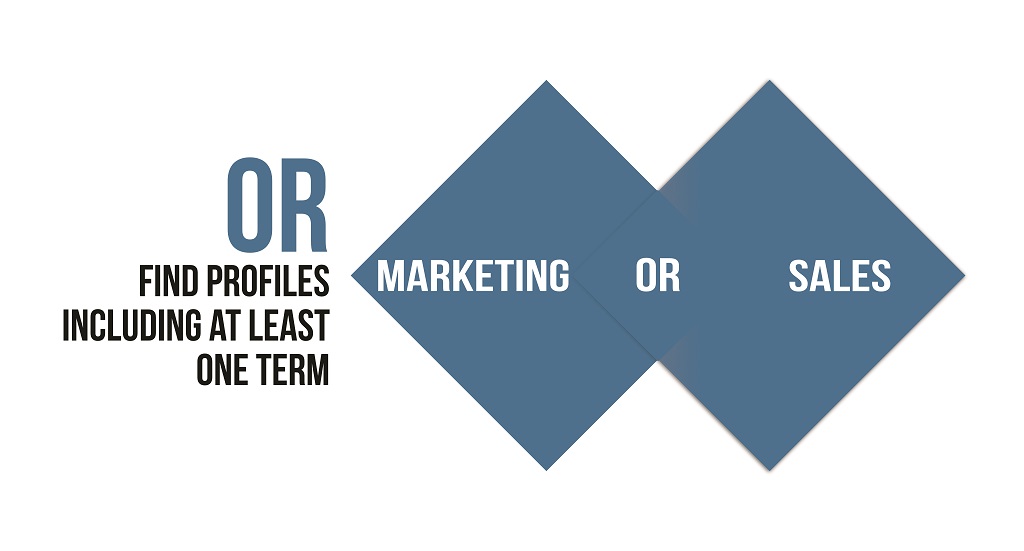
3. OR
The OR operator is used when you want results of either one or both search keywords. This operator is useful when you want to broaden your search and include multiple search terms that are similar in meaning. For example, if you are searching for candidates working as software developers and want to find those working in Financial Services or the Government sector. You can use the OR operator to combine these search terms.
The search query would look like this: “Software Developer” AND (“Financial Services” OR “Government Services”).
This would give candidate profiles that contain the search term “Software Developer” and either “Financial Services” or “Government Services”.
Some other examples include:
- Marketing OR Sales
- “Marketing Manager” OR “Sales Manager”
4. NOT
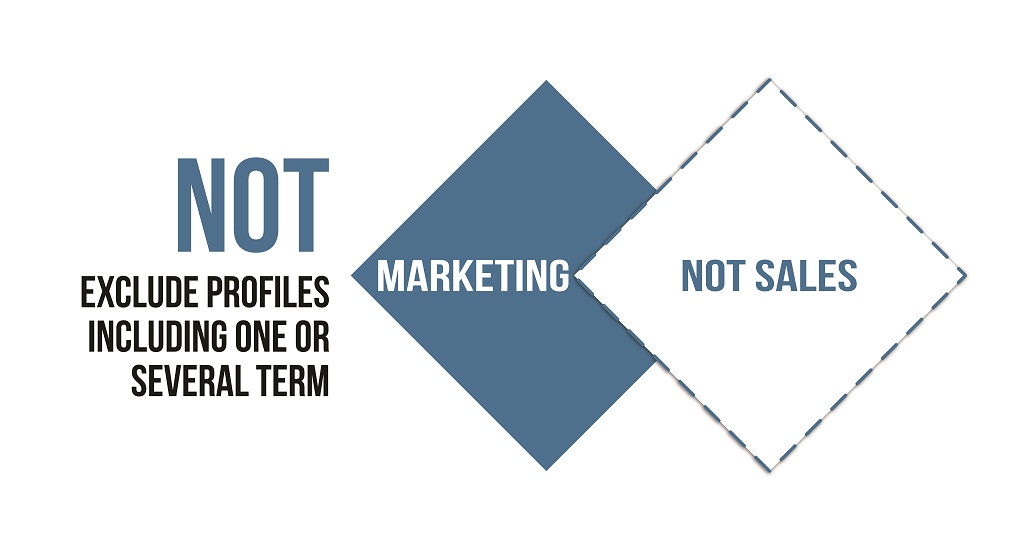
The NOT operator is used when you want to exclude specific search keywords from your search results. This operator is useful when you want to narrow your search results and exclude certain terms that may not be related to your search. For example, if you are searching for candidates working as software developers and want to exclude candidates’ profiles containing the term “fresher”, you would use the operator NOT to exclude this term.
The search query would look like this: “Software Developer” NOT “Fresher”
This would provide only the candidate profiles that contain the search term “software developer” and do not contain the term “fresher”.
Some other examples include:
- Marketing NOT Sales
- “Marketing Manager” NOT “Sales Manager” NOT B2C
5. Parentheses – ()
Parentheses are used to group search terms together and create more complex search queries. This is especially helpful when you want to combine multiple operators. For example, if you are searching for candidate profiles working as software developers and want to find those working in either Financial Services or Government Services sectors, but you want to exclude any profile containing the term “junior”, you would use parentheses to group the search terms.
The search query would look like this: (“Software Developer” AND (“Financial Services” OR “Government Services”)) NOT “Junior”.
This would provide only the candidate profiles that contain the search term “software developer” and either “Financial Services” or “Government Services”, and do not contain the term “junior”.
Some other examples include:
- Manager AND (Sales OR Marketing)
- Marketing Manager (B2B OR B2C)
Mastering the above-mentioned Boolean search operators can help greatly improve the accuracy and relevance of your LinkedIn search results. You can now find the information you need more quickly and efficiently and gain a competitive edge in your job search or professional networking efforts.
What are the Key Benefits of Using Boolean Search?
From saving time to providing targeted search results, LinkedIn Boolean search proves to be highly beneficial for businesses. Some of the key benefits include:
1. Refined Search Results
LinkedIn Boolean search helps you to get targeted search results by combining multiple search terms and operators. This can help you quickly find the most relevant individuals that meet your criteria ranging from job title and company name to area of specialization and talent. So, you can now directly land on the relevant results rather than scrolling through many pages of irrelevant results.
2. Time Saving
By providing more accurate and relevant search results, Boolean search helps you save a significant amount of time. With the ability to use operators such as AND, OR, and NOT, you can easily filter out irrelevant results and focus on the most useful ones.
3. Competitive Advantage
By mastering LinkedIn Boolean search, you can gain a competitive edge over other users who are not familiar with the technique. This helps you find opportunities and connections that others might miss.
4. Access to Hidden Information
LinkedIn comprises a massive amount of information, but only a small portion of it is easily accessible through the platform’s search features. By using Boolean search, you can uncover hidden information and gain access to people, jobs, and other data that may not be readily visible on the surface.
5. Improved Networking
Boolean search can help you find and connect with like-minded professionals with similar interests or career goals. This can help you expand your network and make prominent connections, resulting in new opportunities or collaborations.
Overall, mastering Boolean search on LinkedIn can help you achieve your career or business goals more efficiently and effectively by providing you with targeted, relevant, and actionable information.
What are the Key Instructions to Follow While Using Boolean Search?
One must follow certain instructions to tap the full potential of LinkedIn Boolean Search. Here are some of them:
- The Boolean search operators, including OR, AND, and NOT must be used in upper case. For example, Manager AND Director
- If your search keyword is more than one work, you must include it in quotation marks. For example, “Senior Manager” AND Director
- While using multiple Boolean operators in your search query, use parenthesis. For example: (“Director” AND Senior Manager) NOT “Sales Executive”
- Wildcard searches like “*” are not supported.
- Only standard, straight quotation marks (“) are supported in LinkedIn searches. Curly quotes (“) are not supported.
- For Recruiter and LinkedIn.com, the Boolean search is supported in the keyword field, whereas for Sales Navigator, it is supported in the title, company, and keyword fields.
- LinkedIn does not support using the + sign for AND and – sign for NOT operators.
Where to Use Boolean Search on LinkedIn
As mentioned in the earlier sections, one can use LinkedIn Boolean search in three places, namely:
- LinkedIn Basic Search
- LinkedIn Sales Navigator Search
- LinkedIn Recruiter Search
For these search engines, the Boolean search can be leveraged in the following filter fields:
- First Name
- Last Name
- Job title
- Company
- School
- Keyword
Let’s dig deep into the details:
1. LinkedIn Basic Search
In LinkedIn basic search, you can use the Boolean search operators in the following fields:
- General search
- First Name
- Last Name
- Title
- Company
- School
While the general search looks into the whole profile, the keyword filter will look into specific fields. However, you can’t use quotes on LinkedIn basic search.
2. LinkedIn Sales Navigator Search
In LinkedIn Sales Navigator, you can use Boolean search operators in the following fields:
- The global keyword search
- The current job title search
The global keyword search will search for the keywords in the whole profile, while the current job title search will only look for keywords in the current job experiences of your prospects.
You can also use Boolean search in the Sales Navigator’s Current Company, Past Company, and School fields.
3. LinkedIn Recruiter
One can use Boolean search operators on LinkedIn Recruiter in the following fields:
- Keyword Search
- Job Title Search
- Company Search
- School Search
Best Practices to Use the Boolean Search on LinkedIn
LinkedIn Boolean search is a powerful tool to connect with potential customers and candidates and grow your business. However, creating a super-targeted LinkedIn Boolean search requires a strategic approach. Let’s discuss the best practices for creating a super-targeted Boolean search on LinkedIn.
1. Determine Your Potential Profiles
The first and foremost step to creating a super-targeted LinkedIn Boolean search is to define your potential user profile. You need to clearly understand who your ideal clients or candidates are before you start using LinkedIn filters and Boolean searches. Take time to create a persona and translate it into LinkedIn filters. This will enable you to narrow your search results and focus on the right audience.
2. Analyze Your Existing Profiles
One of the best ways to start drafting your Boolean search query is to analyze the profiles of your current prospects or clients. You need to look into their job titles and keywords that come up most often in their profiles. This will help you get a deep understanding of the type of people you should target. Once you have identified the most relevant job titles and keywords, include them in your Boolean search query.
3. Note Down Your Boolean Query
Writing a long Boolean query directly in a LinkedIn search can be frustrating, as it often gets deleted, and you cannot see the whole expression. Instead, it’s better to write your Boolean query in a Word document or Excel and then paste it into LinkedIn. This will help you to spot potential errors and make any necessary corrections before pasting it into LinkedIn. Also, writing it outside of LinkedIn makes it easy to edit and refine the query as needed.
4. Keep Refining Your Query
Your Boolean query is not something that should be written in stone. It should evolve as your business grows and as you gain a deep understanding of your target audience. Every time you search, you may find irrelevant profiles. To exclude such profiles, add them to your blacklist using NOT. Similarly, you may find new keywords or job titles that you had not thought about initially. Add such profiles to your targeted keyword lists with the OR operator. Keep refining your Boolean query as you understand more about your audience.
By following these best practices, you can create a highly targeted and effective Boolean search to help you connect with the right audience and grow your business on LinkedIn.
LinkedIn Boolean Search Template
Now, let’s look into a Boolean string formula to help you understand the Boolean principle and produce more relevant and accurate results. Here you go:
Template: (Position Keywords) AND (Field Keywords) NOT (Backlists)
This Boolean search string simultaneously searches and eliminates many job titles. For instance, let’s say you are looking for some senior-level employees from the sales and marketing department and exclude other profiles.
First, add the position keywords below:
(“Marketing Manager” OR “Senior Manager” OR “Sales Manager” OR Head )
Then add the field keywords as below:
(Marketing OR Sales)
And add the blacklist keywords as below:
(“Chief Executive Officer” OR CEO OR Founder)
Then combine all the strings into the template:
(“Marketing Manager” OR “Senior Manager” OR “Sales Manager” OR “Sales Head” OR “Marketing Head”) AND (Marketing OR Sales) NOT (CEO OR “Chief Executive Officer” OR Founder OR “Co-Founder” OR “Cofounder”)
Using this Boolean search, the LinkedIn search engine provides the users whose profile contains the following terms:
- Marketing Manager
- Senior Manager
- Sales Manager
- Sales Executive
- Head of Sales
- Head of Marketing
- Marketing Executive
And the search will exclude any profiles, including the words – CEO, Chief Executive Officer, Founder, Co-Founder, and Cofounder.
In Conclusion
Now, we are clear about how LinkedIn Boolean search is a powerful tool in helping you find the right people, job opportunities, and information on the platform. However, it’s important to take the time to define your ideal customer profile and iterate your search query to achieve the best results. While it can seem challenging at first, with practice, you can become a master at crafting super-targeted searches on LinkedIn. You can now take your Boolean searches to the next level and make better hiring decisions. Don’t miss out on the power of LinkedIn Boolean search – try it and see how it can transform your business.

